science(overview)
- Details
- Written by: web web
- Category: Science
- Hits: 1153
science(overview)
Science
Discovering and developing the next generation of allosteric small molecule therapies
Allosteric binding occurs when a molecule binds to a protein at a site other than the enzyme’s active site where the enzyme typically performs its function. The term comes from the Greek word for other site”. This allosteric interaction leads to a conformational change of the protein, which changes the protein's affinity for a substrate.
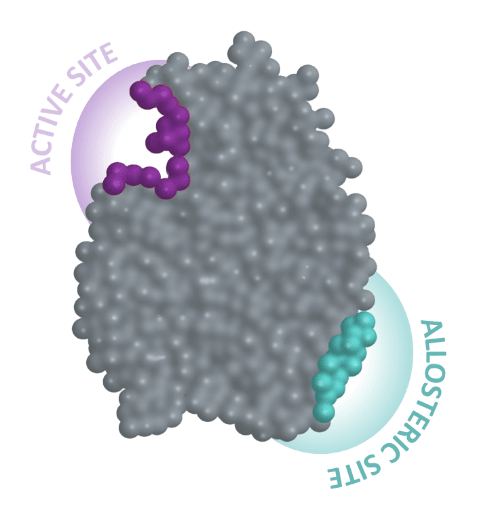
Traditional drugs bind to the Active Site
- Competition with natural substrate can limit efficacy
- More off-target effects as sites are highly conserved across many proteins
Gain’s drugs target Allosteric Sites
- Non-competitive with natural substrate
- Highly specific and better drug properties
- Expands target universe
Allostery offers a degree of control that is unattainable when targeting the active site, allowing researchers to fine-tune how a drug will alter the activity level of a specific protein in a specific disease. Gain’s allosteric modulators are disease-agnostic and designed to modulate a protein to restore or disrupt function as needed via stabilization, destabilization, degradation, inhibition or activation.
